Pregnancy brings with it a new level of caution regarding food choices. The safety of what you consume is vital for your health and the healthy development of your baby. One common debate centers around the safety of eating over easy eggs during pregnancy, especially considering that this cooking method leaves the egg yolk runny. Is it safe? What risks are involved, and how can you still enjoy eggs without compromising your health? Let’s explore these questions in greater detail.
Table of Contents
- What Are Over Easy Eggs?
- The Risk of Salmonella in Over Easy Eggs
- Is it Safe to Eat Over Easy Eggs in the First Trimester?
- How Can You Safely Enjoy Eggs During Pregnancy?
- What Are the Benefits of Eating Fully Cooked Eggs During Pregnancy?
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- Conclusion: Is It Safe to Eat Over Easy Eggs During Pregnancy?
What Are Over Easy Eggs?
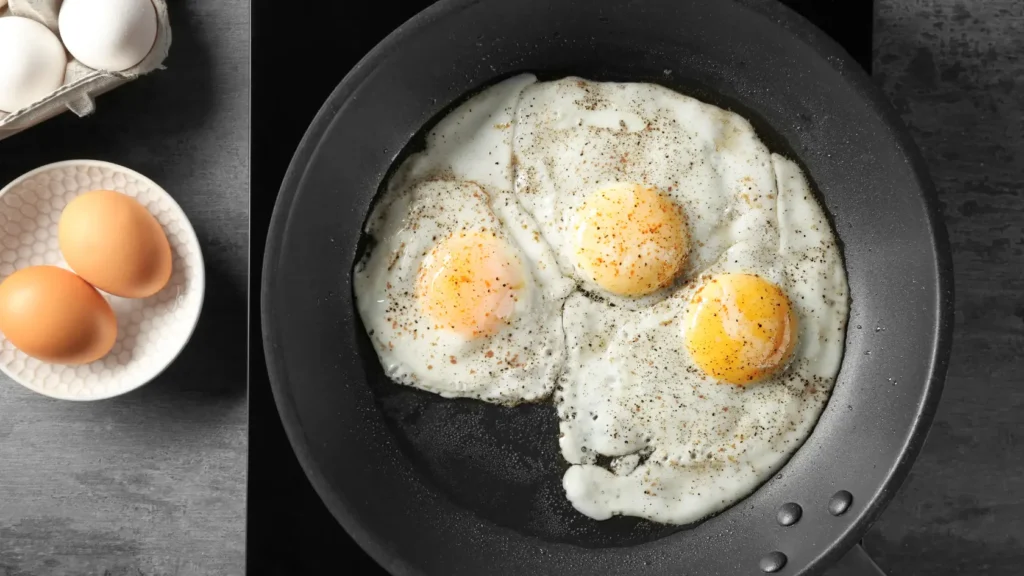

Before we address the safety concerns, let’s review what over easy eggs are and how they’re typically cooked.
An over easy egg is fried on one side until the white is set, but the yolk remains runny. The egg is then carefully flipped and cooked on the other side briefly to ensure the whites are fully cooked, but the yolk stays soft and gooey. The dish is popular due to its delicate texture and slightly runny yolk, which many people find delicious.
However, this cooking method exposes the egg yolk, and that’s where the potential risks begin. The undercooked yolk can harbor harmful bacteria like Salmonella, which presents a specific concern during pregnancy.
The Risk of Salmonella in Over Easy Eggs
Salmonella is one of the most common foodborne illnesses. It is often associated with consuming raw or undercooked eggs. When eggs are not cooked thoroughly, the bacteria present in the yolk can survive and potentially infect the person eating them.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) notes that approximately 1 in every 20,000 eggs may carry Salmonella. However, this statistic varies based on factors such as the egg’s source, storage, and handling. In a typical over easy egg, the yolk is still slightly raw, leaving a higher risk of exposure to salmonella.
1. Dehydration from Diarrhea and Vomiting, Which Can Affect Both You and Your Baby
If you contract salmonella from undercooked foods like over easy eggs, it can cause symptoms like diarrhea and vomiting, leading to dehydration. Mothers who are dehydrated may experience weakness, headaches, dizziness, exhaustion, and kidney issues, which may necessitate medical attention. Dehydration can cause problems with the baby’s nutrient and oxygen supply, which may have an impact on long-term health, as well as reduce amniotic fluid, which can affect fetal growth and development. For the sake of both the mother’s and the unborn child’s health, it is crucial to stay hydrated during pregnancy, particularly in the later stages.
2. Premature Labor if the Infection Becomes Serious
Extreme cases of salmonella infection may lead to premature birth. The condition leads to inflammation of the whole body, including the uterus, which can result in contracting, making it more likely to give birth prematurely. If left untreated, the disease may worsen, leading to further complications for both the mother and the baby. Over easy eggs, with their undercooked yolks, increase the risk of salmonella exposure, which can result in complications like premature labor, preterm birth, and the baby may face health issues associated with being born too early, including lung and brain problems.

3. Miscarriage or Stillbirth in Extreme Cases, Though This Is Rare
Rarely, untreated salmonella infections can result in stillbirth or miscarriage. Sepsis, which can have a serious effect on the pregnancy and raise the risk of a miscarriage or stillbirth, can result from the disease spreading to the bloodstream. As the undercooked yolk may contain salmonella, the risk of these serious consequences is higher if over easy eggs are consumed while pregnant. Even though this is an extreme situation, it is important to reduce the risk for the mother’s and the unborn child’s safety by avoiding undercooked eggs during pregnancy, particularly in the first trimester.
4. Infection in Newborns, Which May Cause Complications and Require Hospitalization
Infections of new-borns with Salmonella may lead to severe health problems such as sepsis, meningitis, pneumonia, or dehydration, and such cases must be hospitalized and treated as an emergency. To overcome the infection, the baby might need antibiotics, fluids, and probably a stay in the neonatal intensive care unit (NICU). Salmonella can be transferred to the unborn child during pregnancy or delivery, resulting in infection shortly after birth. Over easy eggs pose a higher risk of salmonella, making it essential for pregnant women to avoid them to reduce the chances of infection for both mother and baby, especially after birth.
In summary, over easy eggs pose a risk of salmonella infection, which can lead to dehydration, premature labor, miscarriage, and complications for the newborn. It’s best to avoid undercooked eggs during pregnancy for both mother and baby’s safety.
Is it Safe to Eat Over Easy Eggs in the First Trimester?
The first trimester is a critical period in your pregnancy when your baby’s organs are forming. Because the risk of complications from foodborne illnesses is higher during the early stages of pregnancy, the first trimester is when you should be especially cautious with your food choices.
During the first trimester, your immune system is still adapting, and any infections, including foodborne ones, can be more dangerous. For this reason, many obstetricians recommend avoiding over easy eggs (or any egg preparations with runny yolks) during this crucial period.
In fact, the risk of contracting salmonella is not confined to the over easy egg; other raw or undercooked foods like sushi, soft cheeses, and unpasteurized dairy should also be avoided during the first trimester. The consequences of infections in early pregnancy can be devastating, so it’s essential to follow all food safety recommendations closely.
How Can You Safely Enjoy Eggs During Pregnancy?
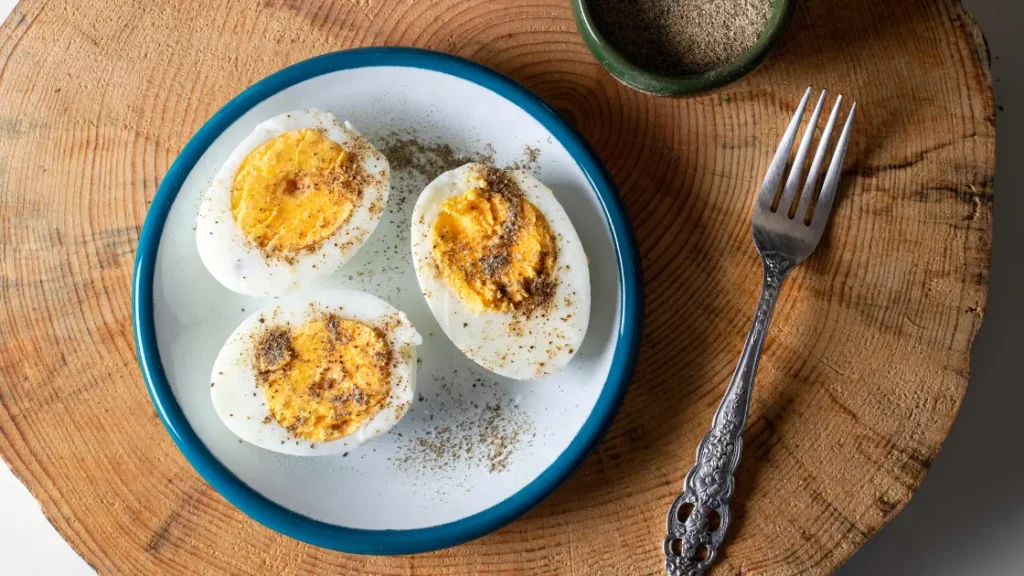

Even though over easy eggs are generally not recommended during pregnancy due to the risk of undercooked yolks, that doesn’t mean you need to give up eggs entirely. Several alternatives allow you to enjoy eggs safely:
1. Fully Cooked Eggs
To ensure that you eliminate the risk of salmonella, you can cook your eggs until both the whites and yolk are fully firm. This entails cooking the egg by frying, scrambling, or hard-boiling it. The key is ensuring that the egg whites and yolk are firm and not runny. In this way, you are still able to eat a tasty meal high in protein without having to worry about bacteria contamination.
2. Pasteurized Eggs
One of the safest alternatives to traditional eggs is pasteurized eggs. These eggs are specially treated to kill harmful bacteria like Salmonella without cooking the egg itself. This is done so that the eggs are safe to consume raw or lightly cooked i.e. you can eat an overeasy egg or similar meals without any worries of bacteria. Many supermarkets offer pasteurized eggs, usually marked as such on the carton.
Pasteurized eggs are also great for preparing foods like homemade mayonnaise, Caesar salad dressing, or eggnog, where raw eggs are traditionally used.
3. Cook Your Eggs with Healthier Cooking Methods
Another way to safely enjoy eggs during pregnancy is to opt for healthier cooking methods. Scrambled eggs, poached eggs, and omelets are great alternatives to over easy eggs. Just cook the eggs all through so the yolks and whites are set.
For an added benefit, you can add vegetables, lean meats, or whole grains to your scrambled eggs or omelets to boost the nutritional value. This way, you can enjoy eggs as part of a balanced and safe pregnancy diet.
What Are the Benefits of Eating Fully Cooked Eggs During Pregnancy?
During pregnancy, eggs are a great source of vital nutrients that support both your health and the growth of your unborn child. The following advantages are present in fully cooked eggs (yellow and whites):

Protein:
Throughout pregnancy, eggs are a great source of high-quality protein that is necessary for maintaining your own muscle strength as well as for repairing cells, constructing tissues, and promoting the growth of the unborn child. This protein also helps to increase energy levels in general.
Choline:
One of the best sources of choline, which is essential for your baby’s brain development and neural function, is eggs. A healthy neural tube is essential for preventing congenital disabilities, and consuming enough choline during pregnancy can support your unborn child’s cognitive development.
Vitamins and Minerals:
Vitamins A, D, and B vitamins, which are vital for both fetal development and personal health maintenance, are abundant in eggs. These nutrients are essential for supporting bone health, improving skin health, increasing immunity, and aiding in the synthesis of red blood cells.
Healthy Fats:
Omega-3 fatty acids are among the healthy fats that are present in enriched eggs. In addition to being vital for the development of your unborn child’s brain and eyes, omega-3 fatty acids also support healthy skin, hair, and cardiovascular health in both the mother and the unborn child by lowering inflammation during pregnancy.
Iron:
Good sources of iron include eggs, which are necessary for the production of hemoglobin in the blood. This helps your baby and you both get oxygen. In order to avoid anemia, which can result in weakness and exhaustion, iron is especially crucial during pregnancy.
Calcium:
Eggs contain a small amount of calcium, which is good for maintaining bone health even though they don’t contain a lot. A healthy prenatal diet promotes the mother’s bone health, and calcium is necessary for the development of the baby’s bones and teeth.
Zinc:
Another mineral found in eggs, zinc is essential for protein synthesis, immunological response, and cell division. For the baby’s development, zinc is especially important for growth and the immune system.
Here’s a comparison table outlining the nutrients in 1 Over Easy Egg vs. 1 Fully Cooked Egg:
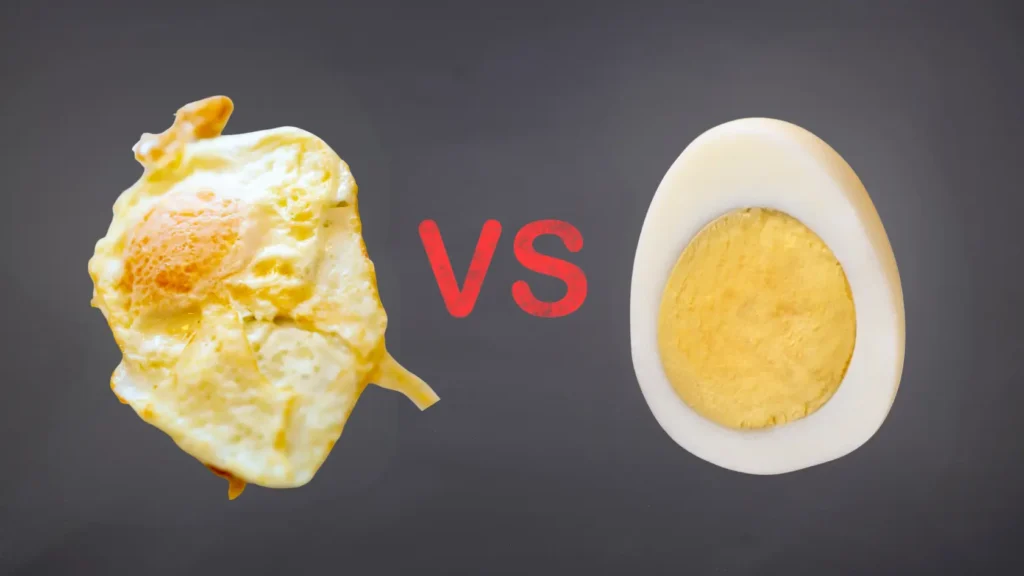
|
Nutrient |
Over Easy Egg (1 egg) |
Fully Cooked Egg (1 egg) |
|
Calories |
90-100 kcal |
70-80 kcal |
|
Protein |
6 grams |
6 grams |
|
Total Fat |
7 grams |
7 grams |
|
Saturated Fat |
2 grams |
1.5 grams |
|
Cholesterol |
180 mg |
180 mg |
|
Carbohydrates |
1 gram |
1 gram |
|
Fiber |
0 grams |
0 grams |
|
Sugars |
0 grams |
0 grams |
|
Vitamin A |
270 IU |
270 IU |
|
Vitamin D |
41 IU |
41 IU |
|
Calcium |
28 mg |
28 mg |
|
Iron |
0.9 mg |
0.9 mg |
|
Omega-3 Fatty Acids |
100 mg |
100 mg |
Key Differences:
- Calories: A fully cooked egg may have slightly fewer calories due to the absence of added oil or butter used in cooking an over easy egg.
- Saturated Fat: Over easy eggs typically contain a slightly higher amount of saturated fat, especially if cooked with butter or oil.
- Nutrient content: Both eggs offer similar amounts of protein, vitamins, and minerals.
This comparison is based on a typical large egg and may vary slightly depending on how the egg is prepared and the cooking method used. By making sure the eggs are cooked through as your and your baby’s safety comes first.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Can I eat over easy eggs if they’re pasteurized?
Yes, pasteurized eggs are safe to eat even if they’re lightly cooked or runny. These eggs have been treated to kill harmful bacteria like Salmonella while keeping the egg raw.
Are there any other egg preparations I should avoid during pregnancy?
Along with over easy eggs, you should avoid consuming raw or undercooked eggs in dishes such as eggnog, homemade mayonnaise, or uncooked cookie dough. These foods can increase the risk of salmonella.
How do I ensure eggs are fully cooked?
To fully cook eggs, ensure both the whites and yolks are firm. When frying or scrambling, cook the eggs until there is no liquid yolk remaining. For hard-boiled eggs, cook them for 10-12 minutes until the whites and yolks are solid.
What happens if I accidentally eat an undercooked egg during pregnancy?
In the event that you inadvertently consume an undercooked egg while pregnant, get in touch with your doctor. They can offer advice and might suggest keeping an eye out for signs of a foodborne illness. Complication risk can be decreased by early intervention.
Conclusion: Is It Safe to Eat Over Easy Eggs During Pregnancy?
Over easy eggs, as well as any eggs with runny yolks, run the risk of salmonella contamination, which can cause serious health problems during pregnancy even though eggs are a nutrient- and protein-dense food. During the first trimester, it is especially crucial to avoid foodborne illnesses because the undercooked yolk of an over easy egg may contain harmful bacteria.
Avoiding over easy egg and other undercooked eggs while pregnant is the best way to stay safe. Choose pasteurized, fully cooked, or other safe substitutes instead. By doing this, you can continue to reap the many health benefits of eggs without endangering the health of either you or your unborn child.
Explore more on Pregnancy Must –