The fetal scalp electrode (FSE) is one of the most significant instruments in contemporary obstetrics for the surveillance of FHR, particularly when conventional external methods are unable to provide accurate or reliable. Information. In order to get more precise heart rate readings during labor, an intrusive device called a FSE is applied directly to the fetal scalp. This detailed guide will explore the use, risks, benefits, and recommendations for FSE, covering everything from FSE placement to potential FSE injury, contraindications, and the best available brands.
What is a Fetal Scalp Electrode?
A fetal scalp electrode (FSE) is a medical device used to measure the fetal heart rate (FHR) during labor. Unlike external monitoring devices that measure the heart rate from the mother’s abdomen, the FSE is a small spiral electrode that is attached directly to the fetal scalp. This method provides more accurate and continuous data on the fetal heart rate and can be particularly useful in complicated or high-risk pregnancies.
How is the Fetal Scalp Electrode Placed?
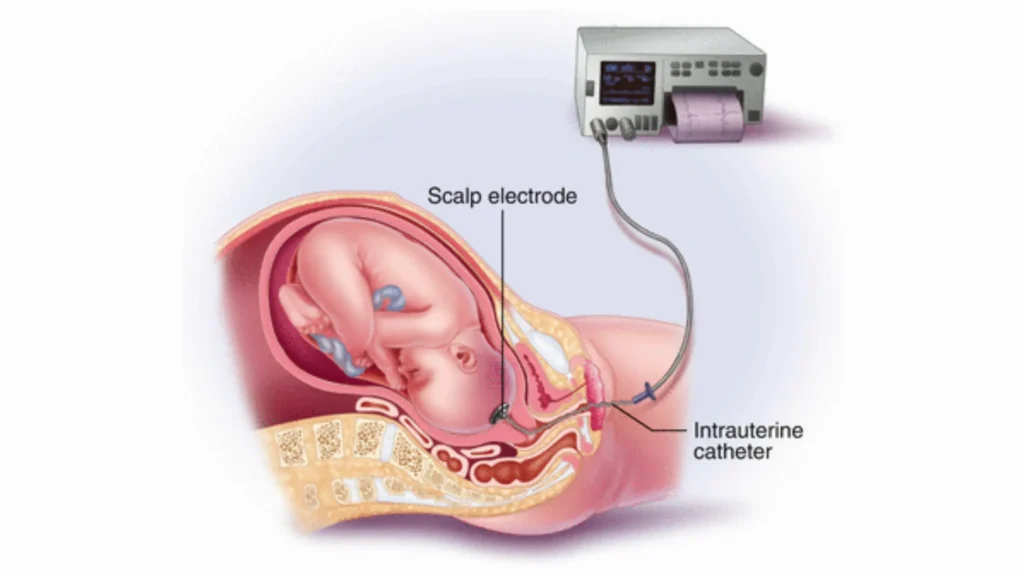
A healthcare professional performs the fetal scalp electrode placement operation during labor to guarantee precise and ongoing fetal heart rate monitoring, particularly in situations where external methods are inadequate.
1. Vaginal Examination
A vaginal examination is performed at the start of the treatment to ensure that the cervix is sufficiently dilated (typically 2-3 cm). For the electrodes to be placed safely, the baby’s head must also be low enough in the birth canal.
2. Positioning the Mother
To provide the provider access to the cervix, the mother is placed on her back with her legs spread and her knees bent.
3. Insertion of the Electrode
The clinician inserts the fetal scalp electrode through the cervix and into the fetal head once the cervix has been dilated. For constant monitoring, the electrode, which contains a tiny spiral, is carefully screwed into the baby’s scalp.
4. Securing and Monitoring
The electrode, which is placed against the baby’s scalp, is hooked up to a monitor that captures the infant’s heart rate 24/7. Therefore, it enables the doctor to monitor the baby’s health throughout the birth.
5. Post-Birth Care
Once the baby is born, the electrode is removed, leaving a small mark on the scalp that usually heals quickly. The healthcare provider will check for any signs of infection or irritation.
Purpose of Using a FSE
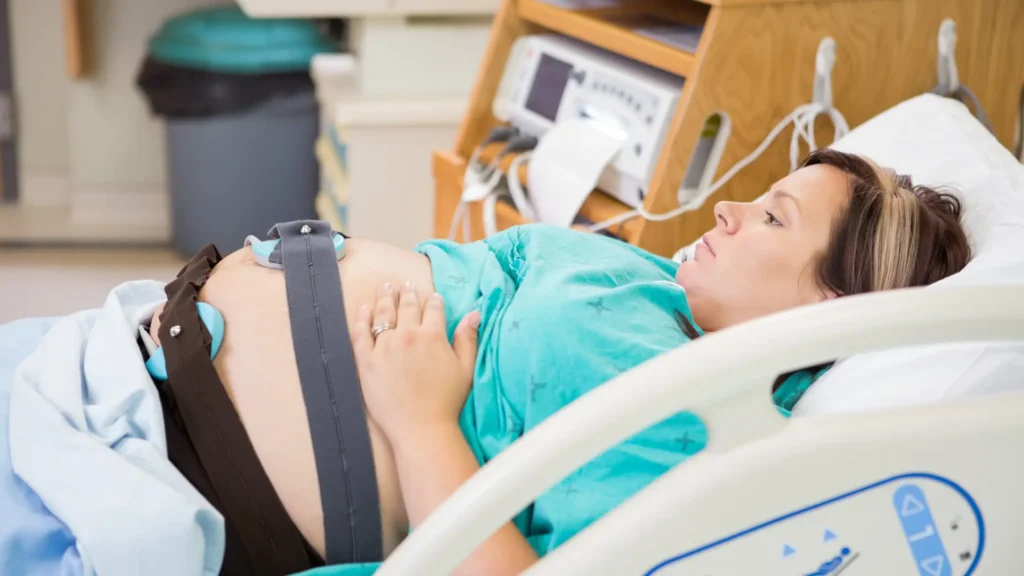
Real-time, precise monitoring of the fetal heart rate (FHR) during labor is the main goal of a fetal scalp electrode (FSE). It is of particular utility when the outer forms of monitoring, such as Doppler ultrasound or even abdominal belts are unhelpful (as they can be when the mother is obese, when the baby moves excessively or when the fetus is incorrectly positioned). The FSE offers direct contact with the fetus, ensuring more reliable data for assessing fetal well-being.
1. Accurate and Reliable Monitoring
If the fetal head has not descended into the birth canal, it may be difficult or unsafe to place the fetal scalp electrode. To have an electrode firmly fastened in the fetal scalp, the head must be in the right place.
2. Effective in Challenging Situations
It is possible that external monitors can fail to pick up the fetal heart in conditions of maternal obesity, excessive pull of the fetus, or abnormal fetal lie. These problems are surmounted by the FSE, which sits on the fetal scalp in a safe way, providing reliable findings under these conditions.
3. Early Detection of Fetal Distress
With high-risk pregnancies, the FSE is vital in detecting fetal distress and giving health care providers real-time data in order to make immediate decisions concerning the situation, including the use of a cesarean section.
4. Invasive for More Reliable Data
Even though external monitors can be unreliable in complex situations, the fetal scalp electrode is the recommended choice for continuous fetal monitoring due to its intrusive nature, which ensures accurate, continuous heart rate monitoring.
5. Informed Decision-Making
The permanent data of the FSE assists the health professionals in making critical decisions during labor, and when a pregnancy is high-risk, the best outcomes possible can be offered to both the mother and the baby.
Fetal Scalp Electrode Injury Risks
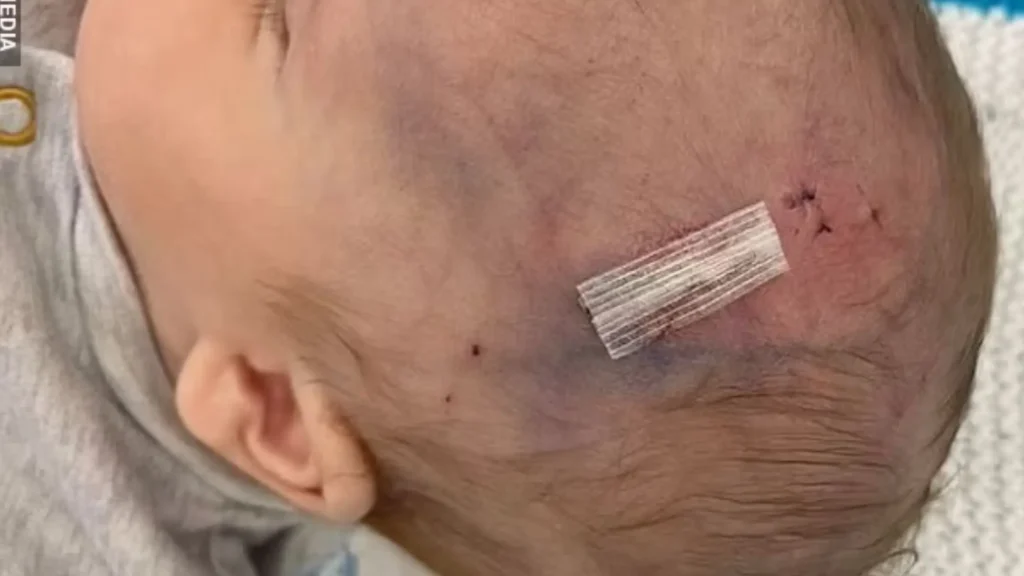
While the fetal scalp electrode (FSE) is designed to minimize risks, there are potential complications associated with its use. The fetal scalp electrode injury is the most frequent risk, and it can happen if the electrode is inserted incorrectly or with too much force.
1. Minor Injuries
The majority of the injuries are small and include cutting or scraping of the scalp of the fetus. These are usually shallow, and they only heal fast, and there are no longevity conditions. These minor injuries are also frequently caused by inappropriate placement or electrode contact with the skin when inserting the electrode.
2. Serious Injuries
In rare cases, if the fetal scalp electrode is left in place for too long or inserted with too much force, more severe complications can arise. They may involve other deeper lacerations or tissue injury, but this is rare.
3. Infection Risks
There is also a risk of infection, especially if the electrode is in place for an extended period or if the insertion process is not sterile. Healthcare providers are trained to monitor for signs of infection or other complications to ensure the safety of the baby.
Contraindications for Using FSE

While fetal scalp electrodes are beneficial in many situations, they are not appropriate for all pregnancies. A number of contraindications exist, which potential users of this technique of fetal monitoring must consider prior to their use of the technique.
1. Preterm Labor
In cases of preterm labor, especially before 34 weeks of gestation, the use of fetal scalp electrodes is generally avoided. Babies born prematurely have thin and fragile skin, which makes placement of electrodes likely to result in complications. Also, the unborn child might not be in a good position in the birth canal to allow ideal placement of the electrode.
2. Infections
The use of a fetal scalp electrode may be contraindicated in the presence of an active mother-to-fetus infection, including HIV, herpetic or other infection capable of fetal transmission. It is recommended external surveillance in such episodes in order to reduce the rate of infection.
3. Unengaged Fetal Head
If the fetal head has not descended into the birth canal, it may be difficult or unsafe to place the fetal scalp electrode. Securely fitting the electrode to the fetal scalp can only be done when the head is in the right position, and this cannot be done when the head is not in the right position.
4. Placenta Previa
The placenta may occur at a low place in the uterus and partly or totally obstruct the cervix due to a condition called placenta previa. This condition can make it risky to insert the fetal scalp electrode, as it could cause bleeding or injury.
Types of FSE and Their Benefits
It’s crucial to select a reputable brand that offers comfort, safety, and accuracy when selecting a fetal scalp electrode. Here is a list of some of the leading producers of superior fetal scalp electrodes for use in medicine.
1. GE Healthcare Fetal Scalp Electrodes
Leading the way in medical technology, GE Healthcare provides a variety of fetal scalp electrodes for precise fetal heart rate monitoring. Their fetal scalp electrodes have a reputation for being dependable, long-lasting, and simple to use. Hospitals all over the world use GE’s electrodes because they work with many of their fetal monitoring systems.
2. Philips Avalon Fetal Monitoring System
The cutting-edge fetal monitoring equipment offered by Philips Avalon is well known. A complete fetal monitoring system that offers consistent, precise readings includes their fetal scalp electrodes. For high-risk pregnancies and challenging labor conditions, Philips’ fetal scalp electrodes are particularly helpful. The company also offers external and internal monitoring options.
3. Medtronic Fetal Scalp Electrodes
The fetal scalp electrodes provided by Medtronic are known for their accuracy and high caliber. Hospitals and birthing facilities are among the healthcare facilities throughout the world that use these electrodes. Medtronic prioritizes dependability and safety, making sure that its fetal scalp electrodes minimize dangers while producing accurate data.
4. Natus Neurology Fetal Scalp Electrodes
Natus provides a variety of fetal monitoring equipment, including fetal scalp electrodes. Their innovative products reflect functionality that brings heart rate monitoring in real-time and the risk of injury is minimal. Natus particularly has a reputation of providing high quality neonatal and pediatric equipment, and is an institution of choice in all hospitals specialized in the care of newborns.
Newborn Fetal Scalp Electrode Scar
After the use of a fetal scalp electrode, a small scar may form on the baby’s scalp where the electrode was attached. This newborn fetal scalp electrode scar is typically minor, as the electrode is designed to cause minimal disruption to the skin.
1. Size and Healing
The scar is usually very small and superficial, fading within a few weeks after birth. Most of the time, it heals without any complications, and no long-term effects are associated with it.
2. Monitoring for Infection
Although the scar is generally harmless, it’s important to monitor the site for any signs of infection or unusual healing. If the area becomes red, swollen, or shows signs of pus, it’s crucial to consult a healthcare provider for proper care.
Alternatives to Fetal Scalp Electrodes
While fetal scalp electrodes provide continuous monitoring, they are not always necessary. External monitoring options such as Doppler ultrasound and abdominal belts are normally the desired choices for low-risk pregnancies since they are non-invasive alternatives.
External Monitoring Methods
1. Doppler Ultrasound
Usually, it is applied in the early phases of labor or during regular examinations. Sound waves bounce off the fetal heart when a probe is inserted on the abdomen to measure the heart rate.
- Advantages: Non-invasive, quick, and easy.
- Limitations: Accuracy can be reduced if the baby is in an awkward position or moving excessively.
2. Abdominal Belts
Abdominal belts use sensors on the abdomen to monitor fetal heart rate and contractions in real time. These are often used during labor.
- Advantages: Comfortable and continuous monitoring.
- Limitations: Less effective if the baby is in a difficult position or the mother has excess abdominal tissue.
FAQ Section
What is a fetal scalp electrode used for?
Fetal heart rate is monitored during labor using a fetal scalp electrode, which yields more precise results than external monitoring techniques, particularly in high-risk pregnancies.
Are there risks associated with FSE?
Yes, there is a small risk of fetal scalp electrode injury, which can result in minor abrasions or cuts to the fetal scalp. However, such injuries are typically superficial and heal without complications.
How is a fetal scalp electrode placed?
The fetal scalp electrode is placed through the cervix and attached to the fetal scalp during a vaginal examination. The electrode is secured by a small spiral that holds it in place.
Can FSE be used on premature babies?
The use of fetal scalp electrodes in premature babies (especially those born before 34 weeks) should be carefully considered. Premature babies have delicate skin, and the electrode may not be suitable in these cases due to the increased risk of injury.
What are the contraindications for using a fetal scalp electrode?
If the fetal head is not engaged, the mother has an active infection, or there is placenta previa or preterm labor, fetal scalp electrodes should not be used.
Final Thoughts
An indispensable instrument for keeping an eye on the health of the fetus during labor, particularly in high-risk circumstances, is the fetal scalp electrode. Healthcare professionals must carefully consider if fetal scalp electrodes are necessary before doing the treatment, even though it is generally safe. The safety of mother and child during labor can be improved by selecting the appropriate brand and being aware of any possible contraindications and harm risks.
Stay updated with every concern that may rise in pregnancy with Pregnancy Must –









