Positional restraint asphyxia is a serious health condition that occurs when someone is held in a position that makes it difficult for them to breathe. It is something that should be known by every kid and not just a term that adults should learn about to make them safe.
In this guide, we’ll explore what positional restraint asphyxia is, how it can happen, why it’s dangerous, and what you can do to stay safe.
Restraint Asphyxia?
Positional restraint asphyxia occurs when someone is placed or held in a position that blocks their airway or prevents normal breathing. In such case, the body cannot receive sufficient amount of oxygen, that it requires to create normal functioning and sustain the health of the said organism.
How It Happens?
The following are some typical causes of positional restraint asphyxia:
- Restricted in enclosed spaces: In confined places, or spaces with objects to one side, you may find that when you are confined then your body may be squeezed and breathing can get difficult. This may occur in such locations as busy rooms, vehicles, or a small area where people can only have a limited movement.
- Physically held down: By being restrained or pinned in one position over a considerable amount of time, this has the ability to pin your chest and diaphragm and hinders the intake of air. This may occur at some point in the implementation of some protection or physical restraint, such as when someone is restrained by another person.
- Lying or sitting improperly: Falling asleep, or sitting down in such a way that obstructs your airway such as; in a face down prone sort of position, can restrict the free passage of the air into the lungs. This closes your breathing capacity causing some difficulty in breathing and this may result in suffocation which can be rectified.
Why Does It Happen?
Positional restraint asphyxia happens because the position someone is placed in prevents their lungs from expanding fully or obstructs their airway. This may happen when the chest is pressed or the head tilted up so that the head cannot move freely, inhaling air and thus reducing the amount of oxygen gas into the body. In case it is not corrected, the restriction can lead to grievous health hazards, including suffocation or damage to the brain due to a lack of oxygen getting to crucial body organs.
Why Is Positional Restraint Asphyxia Dangerous?
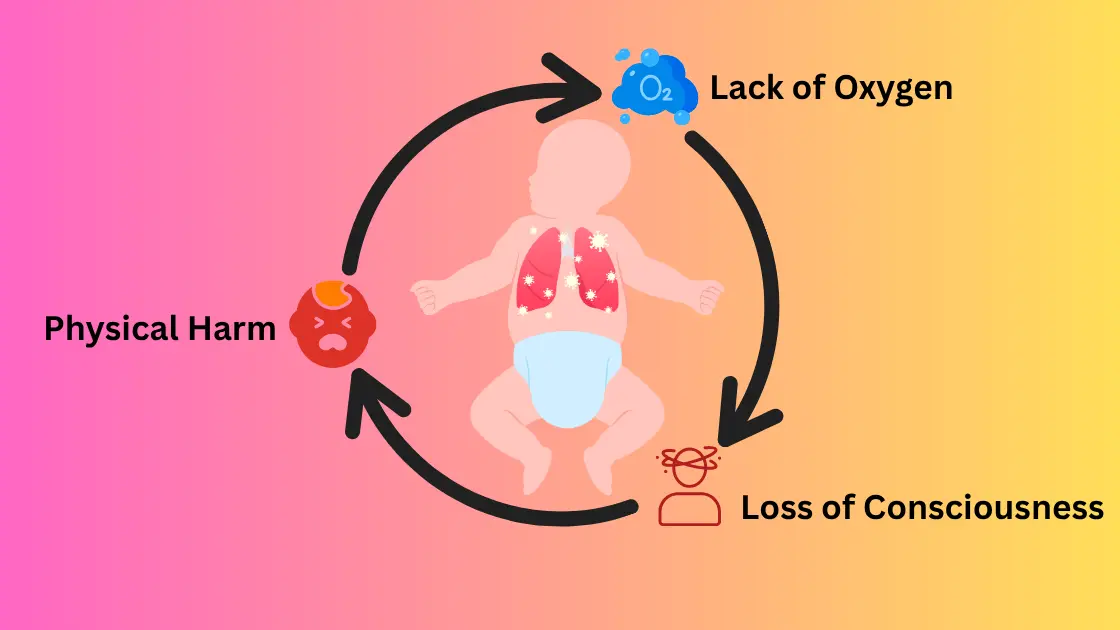
Positional restraint asphyxia is a dangerous condition because it can prevent your body from getting enough oxygen. Almost every single process in your body needs oxygen, including the process of maintaining a healthy brain. Otherwise, major organs begin to fail.
Consequences of Positional Restraint Asphyxia:
• Oxygen deficiency: In case of severe reduction of oxygen in the body, it may lead to serious health problems. The oxygen supply to the organs particularly the brain is essential to carry out its functions. Lack of sufficient oxygen may cause important body parts to start dying out or brain cells to start destroying themselves, and these may have long term effects or even loss of life.
• Fainting: With a large loss of oxygen, the body may not be able to maintain its levels, and this may lead to fainting of the victim or loss of consciousness. This is due to the fact that the brain, which requires oxygen at all times, fails to act in the normal way. It is the warning body system and it says that the body requires some assistance in order to replenish the oxygen levels in the body.
• Physical harm: As a person cannot breathe properly when he/she is bound or surrounded by something, physical harm may also be inflicted. Bruises, cuts or injuries that can be internal are caused by the pressure exerted on the body. In severe cases, pressure applied to some parts and immobility of some parts may last long term and cause physical damage to nerves or other issues.
How Does Positional Restraint Asphyxia Affect the Body?
Here’s how positional restraint asphyxia affects the body in more detail:
| Body Part | How It’s Affected | Result |
| Lungs | The chest might be compressed, making it harder for the lungs to expand fully. | The lungs can’t fill with air properly, leading to difficulty breathing. |
| Airways | If the neck or chest is restricted, the airway can become blocked. | Air can’t flow through the airway, resulting in oxygen deprivation. |
| Blood Circulation | When the body is in a restricted position, blood flow may be limited. | This can cause dizziness, loss of consciousness, or even organ failure. |
| Brain | Lack of oxygen to the brain can cause confusion, dizziness, and unconsciousness. | Oxygen deprivation to the brain can lead to permanent brain damage. |
Who Is at Risk of Positional Restraint Asphyxia?

While anyone can experience positional restraint asphyxia, certain people are at higher risk, especially kids. Children are more susceptible due to the fact that they are still growing and their bodies may not react when they are in a compromising situation. Children will also have higher tendencies of being trapped in confined spaces or being bound in a manner that can hardly enable them to breathe freely. They are also vulnerable to this danger because they are smaller and have less developed capacities to express discomfort.
At-Risk Groups:
• Children: Children are just adventurous and they may find themselves in an area where they cannot move around such as playing in small areas or they are positioned in a way that they cannot move. Their bodies are not fully developed which makes them less able to realize when they are in danger or when they are having problems breathing. Adults should monitor them carefully because they may not be as aware of the dangers as they should be.
• People in certain professions: Emergency workers, law enforcement officers, and healthcare professionals who often have to restrain people for safety or medical reasons must be trained to recognize and avoid positional restraint asphyxia. They must apply proper and safe means of restraint and keep a close supervision so that the person is not placed in a way that makes them breath with difficulty.
• People with certain health conditions: Individuals who have respiratory or cardiovascular issues (like asthma, heart disease, or lung problems) are at a higher risk of experiencing positional restraint asphyxia. These health ailments may already place further stress on breathing, making the position of restriction an added burden that can add difficulties to the intake and circulation of oxygen, resulting in greater dangers that can be amplified.
Table of Contents
- Restraint Asphyxia?
- Why Is Positional Restraint Asphyxia Dangerous?
- How Does Positional Restraint Asphyxia Affect the Body?
- Who Is at Risk of Positional Restraint Asphyxia?
- Signs of Positional Restraint Asphyxia
- How to Prevent Positional Restraint Asphyxia
- How Emergency Workers Prevent Positional Restraint Asphyxia
- FAQ Section
- Conclusion: Positional Restraint Asphyxia
Signs of Positional Restraint Asphyxia
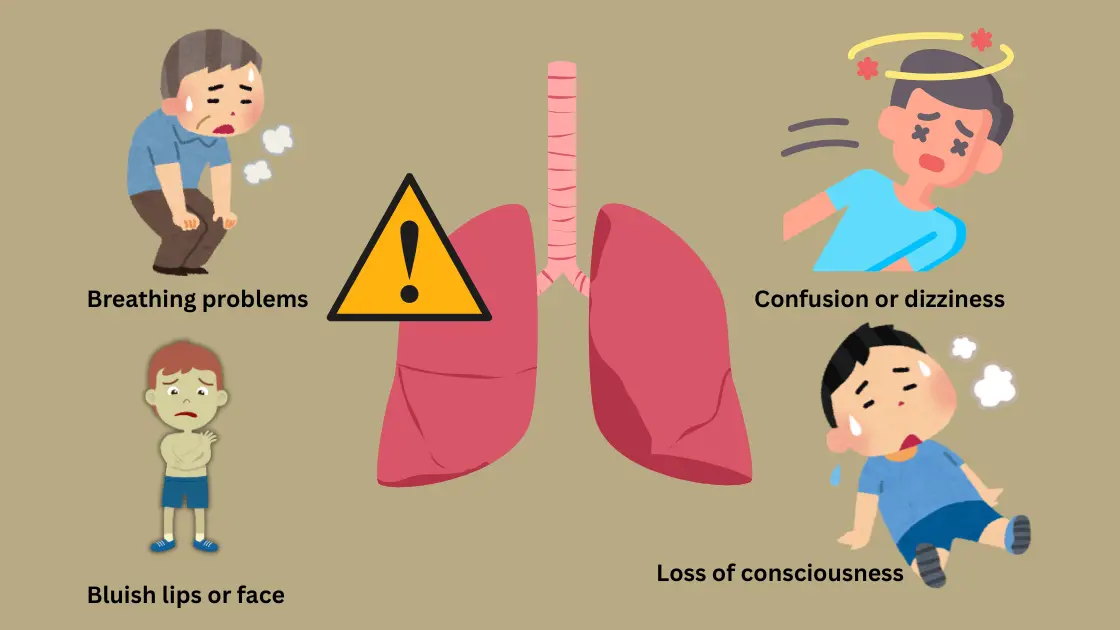
If you or someone else is at risk of positional restraint asphyxia, it’s important to recognize the warning signs early. Such symptoms should be acknowledged and could allow for avoiding severe health outcomes. One list of primary symptoms to be observed is as follows:
• Breathing issues: In case a person is having a hard time breathing or is out of breath, this might indicate to them that there is no sufficient oxygen reach to the body. This occurs when the air passageway becomes obstructed and the lungs cannot expand normally causing one to experience shallow or heavy breathing.
• Bluish lips or face: This indicates the deprivation of oxygen by the bluish tint on the lips, face or extremities. Inadequate supply of oxygen to the body will be followed by the blood supply to these places being affected by the reduced oxygen inside the blood, which makes them turn bluish.
• Confusion or dizziness: The brain depends on oxygen supply and constant oxygen supply is needed to maintain the functionality of the brain. A drop in oxygen levels may influence the work of brain, causing alterations such as confusion, dizziness or even inability to think clearly. This is a grave indication of the body not receiving desired oxygen.
• Lose of consciousness: The lack of sufficient oxygen with prolonged time to the brain may lead to the unconsciousness of the person. It is then that the body enters its protective state since without enough oxygen, the brain cannot perform its role effectively, and therefore you have a case of emergency rescue services being required.
How to Prevent Positional Restraint Asphyxia
Here are some ways to keep yourself and others safe from positional restraint asphyxia:
- Keep yourself comfortable: It is advisable to avoid any posture that may obstruct your breathing channel, such as sleeping on the stomach or face-forward slouched positioning. You must also make sure that you are breathing easily and comfortably, give a fresh posture every now and then when you are sleeping, sitting for a long time, or playing.
- Consciousness in actions: This applies particularly when you are playing any sport or moving to an enclosed place, or you are being involved in a rescue operation; always be conscious of what the body is doing. This is so that in a case where they may restrain you or in a small space, one is able to move or adjust so that they can breathe easily. Never continue doing it if you experience discomfort or tightness, but change position.
- Ask assistance in case of feeling confined: In the event that you or another person feels confined, unable to move or has issues with the breathing, it is best to request a form of help immediately. When you cannot solve the problem yourself get an adult or emergency worker or person in charge who can help in making sure that you can breathe well.
- Training for professionals: For people who are responsible for physical restraint, such as police officers, paramedics, or security staff, it is essential that they undergo proper training on how to avoid positional restraint asphyxia. This involves the knowledge of how to safely restrain a person, identify the early symptoms of difficulties in breathing, and know how to get someone out of restrictive postures without any injury to the person as soon as possible.
How Emergency Workers Prevent Positional Restraint Asphyxia
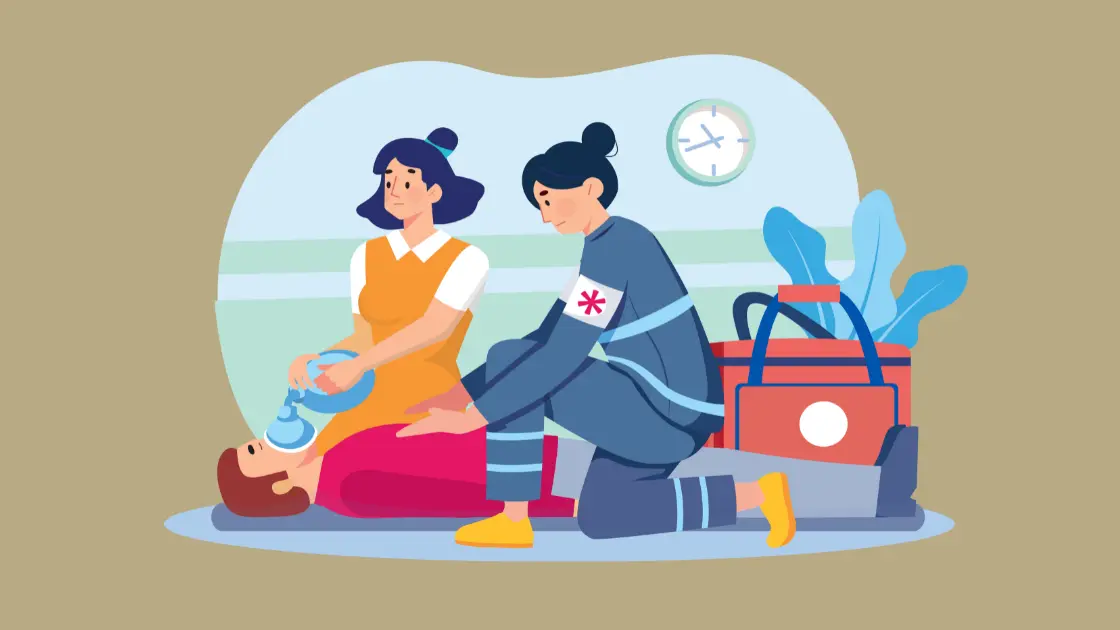

Trained professionals like paramedics, police officers, and other emergency responders are taught how to safely manage situations that may lead to positional restraint asphyxia.
This is the way they go about it:
- The proper restraint mechanisms: The emergency workers implemented during restraint minimize the risk of blocking someone by air way methods that are taught in emergency. This means that the individual to be immobilized should not be placed in a posture that limits his or her chest or neck. Restraint techniques are developed in such a way that the individual is not injured as they are encouraged to breathe and move a little.
- Monitoring: Emergency workers constantly pay attention to the breathing rate, heart rate of a person and his general physical state when he or she is tied or in a potentially harmful position. This allows them to detect any early signs of distress, such as difficulty in breathing or changes in skin colour, so they can intervene quickly to prevent positional restraint asphyxia.
- Positioning: It is essential to place the position properly in order to avoid obstruction in the airways. Emergency workers are taught how to move the body of the individual, which will enable him or her to maximize the air in the chest, keep his waterway open and help to clear his respiratory system. It could include repositioning the individual every so often or applying special methods that could avoid pressure on the chest or neck.
FAQ Section
Q1: What is the most important thing to remember about positional restraint asphyxia?
A1: The most important thing to remember is that positional restraint asphyxia is dangerous because it can stop your body from getting enough oxygen. Never forget to be in a good posture in which you breathe well.
Q2: How do I know if I’m in danger of positional restraint asphyxia?
A2: You may also be at risk when you start feeling shortness of breath, feeling dizzy, or trapped. It is necessary to change the location to one where you can breathe easily and seek assistance immediately.
Q3: Can positional restraint asphyxia be prevented?
A3: Yes! By being mindful of your position, staying aware of how you’re sitting or lying down, and asking for help if needed, you can avoid the dangers of positional restraint asphyxia.
Q4: Is positional restraint asphyxia common?
A4: It cannot occur on a daily basis, but it is something that one should take note of. It may occur when one is physically tied or held in a situation for too long.
Q5: What should I do when I see that someone is struggling with breathing?
A5: Seeing somebody not being able to breathe correctly should be immediately reported to an adult, or the call should be made. The person may be experiencing positional asphyxia, and quick action can save their life.
Conclusion: Positional Restraint Asphyxia
Positional restraint asphyxia is a dangerous condition, but by staying aware and knowing what to do, you can protect yourself and others. It is always a good idea to check your position and be able to breathe. In case you are ever in one of those situations where you find yourself in trouble breathing, ask someone to assist you when you need help.
Keep in mind, while you are keeping yourself safe, you also need to observe how you are positioned, or use caution and look out to others in difficult positions. Let’s make sure everyone knows how to stay safe from positional restraint asphyxia!
Explore more on Pregnancy Must –









