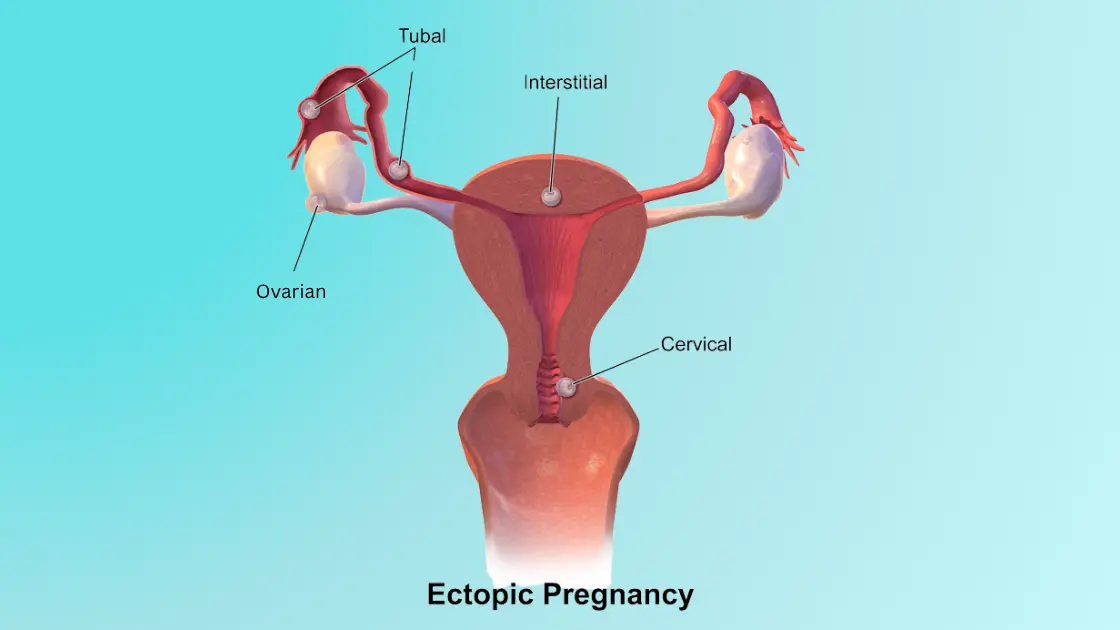
Cornual ectopicpregnancy is a life-threatening situation in which the fertilized egg grows in the corner of the uterus instead of growing in the fallopian tube. This is a rare condition, but it is quite dangerous to the health and future fertility of the mother. It is important to diagnose early and treat accordingly.
Table of Contents
- What is Cornual Ectopic Pregnancy?
- Causes of Cornual Ectopic Pregnancy
- How is Cornual Ectopic Pregnancy Diagnosed?
- Signs and Symptoms of Cornual Ectopic Pregnancy
- Cornual Ectopic Pregnancy and Future Pregnancies
- Treatment Options for Cornual Ectopic Pregnancy
- Cornual Ectopic Pregnancy Risks
- Cornual Ectopic Pregnancy: Prevention and Monitoring
- FAQs
What is Cornual Ectopic Pregnancy?
A cornual ectopic pregnancy occurs when a fertilized egg implants in the cornu or horn of the uterus, which is near the fallopian tubes. This type of ectopic pregnancy can be challenging to diagnose because the symptoms often resemble those of a regular intrauterine pregnancy. But the same can be even more dangerous due to the location of the pregnancy.
Causes of Cornual Ectopic Pregnancy
Cornual ectopic pregnancy may not be clearly understood in terms of its causes. But the risk is enhanced by some factors, among which are:
1. Previous Ectopic Pregnancies
Women who have had a previous ectopic pregnancy are at higher risk of experiencing another one, including cornual ectopic pregnancy. This is because the underlying issues, such as damage to the fallopian tubes or irregularities in the reproductive system, can persist or recur. The scarring of the first ectopic pregnancy or the structural alterations may make it more challenging for the fertilized egg to move to the uterus, which in most cases results in another risk of implantation in a different, unusual location, like the cornual section of the uterus.
2. Infections in the Fallopian Tubes
Infections in the fallopian tubes, often caused by sexually transmitted infections (STIs) like chlamydia or gonorrhea, can lead to scarring or blockages in the tubes. These infections, which can cause pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), make it more difficult for the egg to pass through the tubes to the uterus. As a result, the fertilized egg may implant somewhere outside the uterus, including the cornual region. Fallopian tube infections are a significant risk factor for ectopic pregnancies in general.
3. Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID)
Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) is another infection of the female reproductive organs, which in many cases is the result of inadequately treated STIs. PID may lead to scarring of the fallopian tube, uterus, and ovaries, as well as inflammation of the organs. This damage increases the risk of ectopic pregnancies, including cornual ectopic pregnancy. The reason why implantation may occur out of place and the increase in the risks arises is when the fallopian tubes are scarred or blocked as a result of PID, hence are not able to carry the egg through the reproductive system.
4. Endometriosis
Endometriosis is a condition where tissue similar to the lining of the uterus grows outside of it, often on the ovaries, fallopian tubes, or other pelvic organs. This tissue can cause inflammation, scarring, and damage to the reproductive organs, which increases the risk of an ectopic pregnancy. In cornual ectopic pregnancy, the abnormal tissue growth may affect the movement of the egg or cause the fertilized egg to implant in the cornual region of the uterus, rather than traveling to the uterine cavity.
5. In Vitro Fertilization (IVF) Treatments
In vitro fertilization (IVF) involves fertilizing an egg outside of the body and then implanting it into the uterus. While IVF helps many women conceive, it carries a slightly higher risk of ectopic pregnancy, including cornual ectopic pregnancy. This is because IVF treatments sometimes involve the transfer of embryos to locations outside the ideal implantation zone. In some cases, embryos may implant in the fallopian tubes or cornual region of the uterus, leading to an ectopic pregnancy.
6. Surgical scarring from prior fallopian tube or uterine surgeries
Any past surgeries inside the uterus or fallopian tube, as surgeries conducted to treat fibroids, ectopic pregnancies, or surgery in the pelvis, may cause scarring or anatomical distortion. This scarring can lead to blockage of the fallopian tubes or distortion of the route that the egg should follow to get to the uterus. Cornual ectopic pregnancy is more likely if the tubes are damaged because the fertilized egg may not reach the uterus and may implant in the cornual area. It is frequently recommended that women who have had pelvic surgeries in the past keep a closer eye on their pregnancies in order to identify any issues early.
These risk factors highlight the significance of early pregnancy monitoring and intervention, particularly for women who have had pelvic infections, ectopic pregnancies, or surgeries that may have affected their reproductive organs in the past. Future fertility can be preserved and results greatly improved by early detection of a cornual ectopic pregnancy.
How is Cornual Ectopic Pregnancy Diagnosed?
Cornual ectopic pregnancy is difficult to diagnose and necessitates several tests. Vaginal bleeding or unusual pelvic pain are frequently the first symptoms.
Cornual Ectopic Pregnancy Ultrasound
A cornual ectopic pregnancy ultrasound is one of the most critical diagnostic tools. Ultrasound images help determine the location of the pregnancy. In some cases, the pregnancy may be located in the cornual region, which might not be as obvious as other types of ectopic pregnancies, such as those in the fallopian tube.
Other imaging techniques, such as laparoscopy, might also be used to confirm the diagnosis.
Signs and Symptoms of Cornual Ectopic Pregnancy
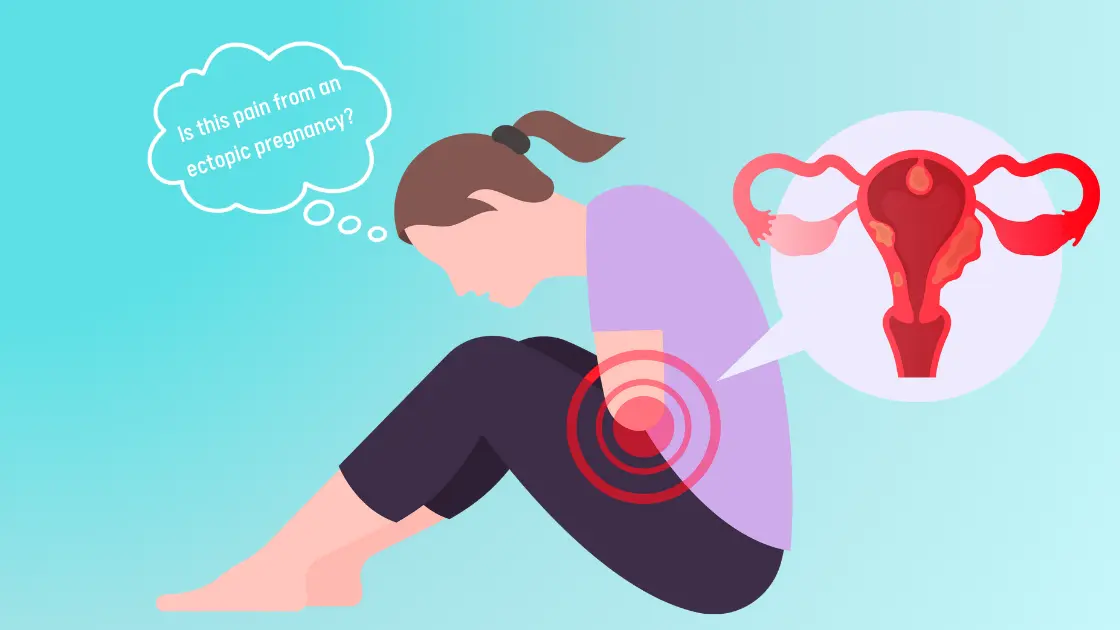

Cornual ectopic pregnancy symptoms can be deceptive, frequently resembling those of other ectopic pregnancies or a typical pregnancy. Typical signs and symptoms include:
1. Severe Pelvic Pain or Cramping
One of the most typical indicators of an ectopic pregnancy, including a cornual ectopic pregnancy, is pelvic pain or cramping. Because the fertilized egg implants outside of the uterus’s normal location, the surrounding tissues are compressed, stretched, or irritated, which results in pain. The fertilized egg implants in the cornu, or uterine corner, close to the fallopian tubes in a cornual ectopic pregnancy, which can cause excruciating pain. The pain may start as mild cramping, but can become severe as the pregnancy grows or if complications like rupture occur.
2. Vaginal Bleeding or Spotting
Vaginal bleeding or spotting is another common indication of a cornual ectopic pregnancy. Since the egg is fertilized at this stage, it can also bleed, and this irritates the rest of the tissues or bursts blood vessels. In certain situations, this bleeding—which can be either light or heavy—can be confused with a typical menstrual cycle. In order to rule out ectopic pregnancy or other complications, any unusual vaginal bleeding should be taken seriously and evaluated by a healthcare professional, especially if it is accompanied by other symptoms.
3. Shoulder Pain Due to Internal Bleeding
Shoulder pain in the context of an ectopic pregnancy is often a result of internal bleeding. If the cornual pregnancy causes the fallopian tube or the surrounding area to rupture, blood can pool in the abdomen. The blood then irritates the diaphragm, which is sensitive to pain. The pain is referred to the shoulder, typically the tip of the shoulder on the same side as the rupture. Such pain is a medical emergency, as this type of pain means that the pregnancy has ruptured and there is some bleeding inside, and so the patient should seek immediate treatment.
4. Dizziness or Fainting (Due to Shock from Internal Bleeding)
Dizziness or fainting can occur if there is significant internal bleeding from a cornual ectopic pregnancy. The bleeding can reduce blood circulation and lower blood pressure, leading to shock, which is a life-threatening condition. Dizziness, lightheadedness, and even fainting can occur when there is a relationship between inadequate blood flow. Unless treated, shock may be fatal, and that is why prompt treatment is important in case any of these symptoms are experienced. This is more troublesome when accompanied by severe pain or shoulder pain, which suggests rupture.
When these symptoms coexist, they are suggestive of a cornual ectopic pregnancy, and prompt medical intervention is required to avoid more complications.
Cornual Ectopic Pregnancy and Future Pregnancies
The possible influence of cornual ectopic pregnancy on subsequent pregnancies is one of the main worries. The uterus and fallopian tubes may be affected, and surgery is frequently necessary to treat the condition. Fertility issues may arise, depending on the extent of the pregnancy and the necessary surgery.
Research suggests that women who have had a cornual ectopic pregnancy may be slightly more likely to have another ectopic pregnancy in the future. However, with timely care and careful observation, many women can have successful pregnancies in the future.
Treatment Options for Cornual Ectopic Pregnancy
The stage of the pregnancy, the intensity of the symptoms, and the presence of complications all influence how cornual ectopic pregnancy is treated. The principal (treating) forms are:
Cornual Ectopic Pregnancy Surgery
Surgical intervention is often required to remove the ectopic pregnancy and prevent life-threatening complications such as uterine rupture. The two most common surgical approaches are:
Laparoscopic Surgery
Using a camera and surgical instruments, laparoscopic surgery is a minimally invasive technique that involves making tiny incisions to remove the cornual ectopic pregnancy. It provides precise excision with minimal damage to the surrounding tissues, and this facilitates a reduction in pain as well as faster healing and reduced scarring.
Hysterectomy
Only in extreme situations where the cornual ectopic pregnancy results in potentially fatal complications, like a ruptured uterus or uncontrollable bleeding, is a hysterectomy—the removal of the uterus—performed. Although it takes care of the immediate danger, this decision leaves one without the possibility of becoming pregnant, and thus it is an option that is applied as the last resort.
Comparison table for Laparoscopic Surgery and Hysterectomy
| Feature | Laparoscopic Surgery | Hysterectomy |
| Procedure Type | Minimally invasive (small incisions, camera-guided) | Major surgery (removal of the uterus) |
| Recovery Time | Faster recovery due to minimal tissue damage | Longer recovery time due to more invasive nature |
| Pain Level | Less pain due to smaller incisions | More pain due to larger incisions and uterus removal |
| Scarring | Minimal scarring (small incisions) | Significant scarring from the removal of the uterus |
| Fertility Impact | Preserves fertility (if no major damage) | Loss of fertility (removal of the uterus) |
| Risk of Complications | Low, with quick recovery if complications arise | Higher risk of long-term complications like infection or hormonal imbalance |
| Indication | Preferred for most cases of cornual ectopic pregnancy | Reserved for severe cases with life-threatening risks |
| Effect on Future Pregnancies | Can allow for future pregnancies | No ability to carry a pregnancy after surgery |
| Risks | Mild infection, bleeding, damage to nearby organs | Infection, hemorrhage, hormonal imbalances |
Medical Management
In some cases, medications like methotrexate may be used to treat an ectopic pregnancy if detected early. However, this option is less common for cornual ectopic pregnancy because the location and blood supply to the pregnancy often complicate treatment.
Cornual Ectopic Pregnancy Risks

Cornual ectopic pregnancy, like all other forms of ectopic pregnancy, carries a number of risks, such as:
1. Uterine Rupture
When the uterus tears due to a cornual ectopic pregnancy, it results in uterine rupture, which causes severe internal bleeding. This is a life-threatening emergency that needs immediate surgery to stop the bleeding and avoid potentially fatal outcomes.
2. Fertility Issues
Damage to the uterus or fallopian tubes due to a cornual ectopic pregnancy or its treatment can affect future fertility. Blocking or scarring along the fallopian tube pathway may make it harder for the egg to reach the uterus, and it could possibly increase the risk of another ectopic pregnancy or following conception problems.
3. Infection
After surgery to treat cornual ectopic pregnancy, there is a risk of infection, which can complicate recovery. Infection may also take place in the uterus or other neighboring organs and may require other drugs, e.g., antibiotics, to avoid further health complications.
Cornual Ectopic Pregnancy: Prevention and Monitoring
While there’s no surefire way to prevent cornual ectopic pregnancy, women who have had previous ectopic pregnancies or have risk factors should undergo early ultrasound screenings to catch the condition early. Prevention can be implemented by having regular gynecological examinations and adhering to a healthy lifestyle, which can also further minimize the risk.
FAQs
1. Can a cornual ectopic pregnancy be prevented?
All the cases cannot be stopped, but early signs and periodic gynaecologic examinations may prevent and control the risks.
2. How is a cornual ectopic pregnancy treated?
Medical intervention may consist of an operation, including laparoscopic extraction of the pregnancy. A hysterectomy may be done in severe cases.
3. What are the risks of cornual ectopic pregnancy for future pregnancies?
Women who experience cornual ectopic pregnancy may face fertility challenges and a higher risk of future ectopic pregnancies, though many can successfully carry future pregnancies.
4. How soon should I seek medical help if I suspect a cornual ectopic pregnancy?
If you experience symptoms like pelvic pain, vaginal bleeding, or dizziness, seek medical help immediately for early diagnosis and treatment.
Explore more on Pregnancy Must –