Nutrition is crucial during pregnancy for the health of the developing fetus as well as the mother. Choline is a crucial nutrient that is frequently disregarded. This guide will explore everything you need to know about how much choline for pregnancy is required, its benefits, sources, supplementation, and how to manage its intake safely.
Table of Contents
What is Choline and Why is it Important for Pregnancy?
Choline is a water-soluble nutrient that plays an essential role in many biological functions, including:
1. Cell Membrane Structure
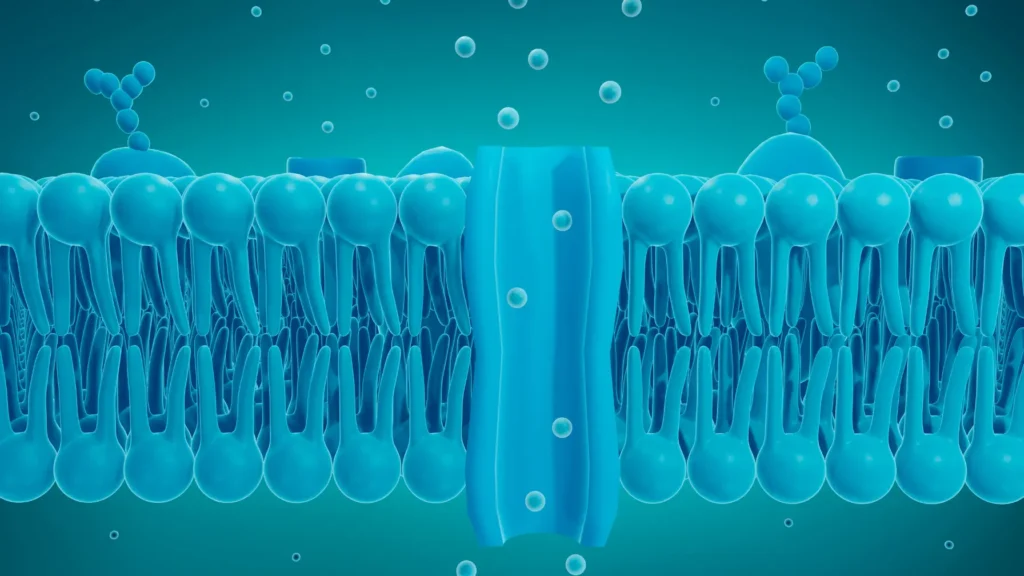
Choline is an essential component of phospholipids, which are a major class of lipids that form the structural foundation of cell membranes. These phospholipids, such as phosphatidylcholine, are vital for the integrity and function of every cell in the body.
Phospholipids and Cell Membranes:
Phospholipids have a unique structure with a hydrophilic (water-attracting) “head” and two hydrophobic (water-repelling) “tails.” With the hydrophilic heads pointing outward toward the water-based environment and the hydrophobic tails pointing inward, their dual nature enables them to form the bilayer structure of cell membranes. By controlling the flow of substances into and out of the cell, this membrane bilayer acts as a protective barrier.
Role of Choline:
Choline is directly involved in producing phosphatidylcholine, which is one of the most abundant phospholipids in the body. The phosphatidylcholine molecule helps to maintain the fluidity, flexibility, and stability of cell membranes. Cell membranes may stiffen in the absence of enough choline, impairing their capacity to carry nutrients, eliminate waste, and preserve intercellular communication.
Impact on Pregnancy: During pregnancy, rapid cell division and growth occur, especially in the developing fetus. Adequate intake of choline ensures that these new cells are able to develop properly and maintain the integrity of the fetal cell membranes, which are important to proper cell growth and development.
2. Fat Metabolism
Choline is also essential in the metabolism of fats in the liver and helps to avoid the build-up of extra fat in the liver, which is a very important organ.
Fat Breakdown and Transport:
One of choline’s primary functions in fat metabolism is as a precursor to phosphatidylcholine, which is required for the synthesis of very low-density lipoproteins (VLDL). VLDL is a type of lipoprotein that helps transport fats (lipids), such as triglycerides, from the liver to other parts of the body. In the absence of adequate choline, the liver cannot effectively produce VLDL, which leads to fat build-up in the liver, a condition known as fatty liver disease.
Prevention of Fatty Liver Disease:
During pregnancy, fatty liver disease can worsen, especially in women who already have a predisposition to gestational diabetes or preeclampsia. Choline helps prevent this build-up by ensuring that the liver can properly export fats, reducing the risk of liver damage, and improving overall liver function.
Choline’s Role in Liver Detoxification:
In addition to breaking down fat, choline is also involved in liver detoxification, which aids in eliminating toxins in the liver to keep it performing its normal duties. In pregnant women, a healthy liver functions are essential to help it increase the overall metabolic needs of the body and clearance of waste products.
3. Brain Development
Because it is a precursor to acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter involved in a number of brain processes, including memory, mood regulation, and learning, choline is essential for brain development, particularly during pregnancy.
Choline and Acetylcholine:
Acetylcholine is one of the key neurotransmitters in the brain. It is involved in synaptic transmission, which is the process by which neurons (nerve cells) communicate with each other. This communication is essential for cognitive functions such as learning, memory, and attention. Choline is used by the body to produce acetylcholine, so sufficient choline levels directly support brain function.
Impact on Fetal Brain Development:
During pregnancy, the fetus’s brain undergoes rapid growth, and choline plays an essential role in this process. Choline helps to form the neural tube, which eventually becomes the brain and spinal cord. As the brain develops, acetylcholine is crucial for the formation of synapses (connections between nerve cells), which are the foundation for memory and learning abilities.
Long-Term Cognitive Function:
Research shows that adequate choline intake during pregnancy is associated with better cognitive outcomes in children later in life. Studies have shown that children born to mothers with higher choline levels tend to perform better on memory tasks and may have better mental development in their early years.
Supporting the Hippocampus:
In addition to breaking down fat, choline is also involved in liver detoxification, which aids in eliminating toxins in the liver to keep it performing its normal duties. In pregnant women, a healthy liver function is essential to help it increase the overall metabolic needs of the body and clearance of waste products.
Memory and Cognitive Performance:
Sufficient choline intake during pregnancy is linked to improved neurogenesis (the creation of new neurons) and better synaptic plasticity (the ability of neurons to strengthen or weaken over time based on experience), both of which are key to memory formation and cognitive abilities. This connection is especially important for fetal brain health, as the groundwork for a child’s cognitive abilities is laid during pregnancy.
During pregnancy, choline becomes especially important because it supports the development of the baby’s brain and spinal cord, the formation of the neural tube, and the overall cognitive health of the baby.
How Much Choline is Needed for Pregnancy?
To get adequate amount of choline it is important to know how much choline is recommended for pregnancy. Because of how important choline is for fetal development, health guidelines place special emphasis on advice for expectant and nursing mothers. Depending on the trimester and whether you are nursing, how much choline for pregnancy for pregnancy is needed by trimester is different.
How Much Choline per Day for Pregnancy
| Pregnancy Stage | Recommended Daily Intake |
| Pregnant Women | 450 mg per day |
| Lactating Women | 550 mg per day |
- 1st Trimester: The neural tube, which will eventually give rise to the baby’s brain and spinal cord, needs 450 mg of choline per day during the early stages of pregnancy.
- 2nd & 3rd Trimester: The baby’s brain and nervous system continue developing rapidly during these stages, so it’s crucial to maintain an intake of 450 to 550 mg daily to support cognitive function and overall brain development.
- Lactation: Breastfeeding women require 550 mg per day, as the body continues to produce essential nutrients that are passed on through breast milk.
What Are the Risks of Choline Deficiency During Pregnancy?
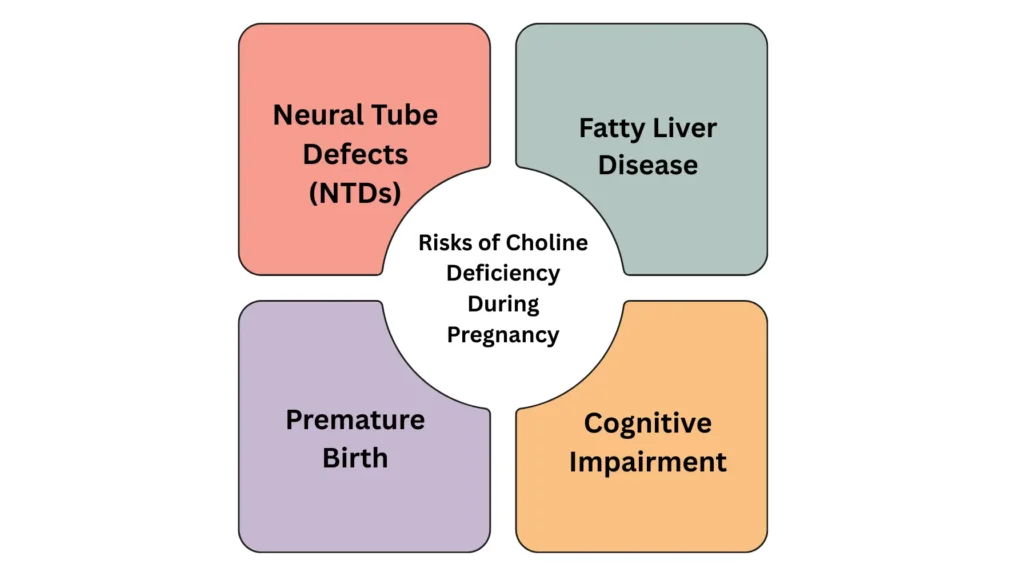
Pregnancy-related choline deficiency can cause major health issues for both the mother and the unborn child. These issues can be serious, so it’s critical to understand the risks:
1. Neural Tube Defects (NTDs)
For the neural tube, which develops into the baby’s brain and spinal cord, to properly close, choline is essential. A lack of choline raises the risk of neural tube defects (NTDs), which include spina bifida, in which the spinal cord does not develop normally. This risk is greatly decreased by eating enough choline, particularly in the early stages of pregnancy when the neural tube is developing.
2. Fatty Liver Disease
Choline aids in the liver’s fat transportation and metabolism. When fat builds up in the liver, a deficiency can result in fatty liver disease, which can cause inflammation of the liver and complications like gestational diabetes or preeclampsia. An adequate intake of choline promotes the health of the mother and the pregnancy as a whole by preventing the accumulation of fat in the liver.
3. Premature Birth
A higher risk of preterm birth has been associated with low choline intake. For the placenta to function properly and deliver nutrients to the baby, choline is necessary. Choline deficiency can impair placental function, resulting in early labor and associated problems like low birth weight and breathing problems.
4. Cognitive Impairment
Memory formation and development of the brain require choline. Deficiencies during pregnancy may affect the cognitive development of the unborn baby, which may lead to learning disabilities and intellectual disability. Enough choline helps support a healthy brain and long-term cognitive function.
How to Meet Your Choline Requirements During Pregnancy

Choline can be obtained through dietary sources, supplementation, or a combination of both. Below are ways to meet your choline needs:
Food Sources of Choline
Choline-rich foods should be an essential part of your pregnancy diet. Below is a breakdown of some of the best natural sources of choline:
| Food Source | Choline Content (mg) | Serving Size |
| Eggs (large) | 147 mg | 1 egg |
| Beef Liver (cooked) | 350 mg | 3 oz |
| Salmon (cooked) | 150 mg | 3 oz |
| Chicken (cooked) | 72 mg | 3 oz |
| Tofu | 35 mg | 1/2 cup |
| Brussels Sprouts | 63 mg | 1 cup |
| Broccoli | 63 mg | 1 cup |
Incorporating Choline into Your Diet
Ensuring adequate choline intake can be easy with a few dietary changes. For example:
- Breakfast: Scrambled eggs with spinach and a side of salmon provide a rich source of choline.
- Lunch: A chicken salad with Brussels sprouts or tofu stir-fry.
- Dinner: Beef liver served with a side of roasted broccoli.
For vegetarians and vegans, plant-based sources such as soybeans, tofu, Brussels sprouts, and broccoli are excellent alternatives.
Choline Supplements
For many pregnant women, it may be difficult to get enough choline through food alone. In such cases, choline supplements can help fill the gap. Here’s how much choline supplement for pregnancy can be taken:
| Supplement Form | Amount per Serving | Recommended Dosage |
| Choline Bitartrate | 250 mg per capsule | 1-2 capsules per day |
| Alpha-GPC | 300 mg per capsule | 1-2 capsules per day |
| Phosphatidylcholine | 100-150 mg per capsule | 1-2 capsules per day |
Important Note: The health provider should always be consulted before you embark on a supplement regimen. They are able to assist you in selecting the correct dosage and form according to your requirements.
Can You Have Too Much Choline During Pregnancy?
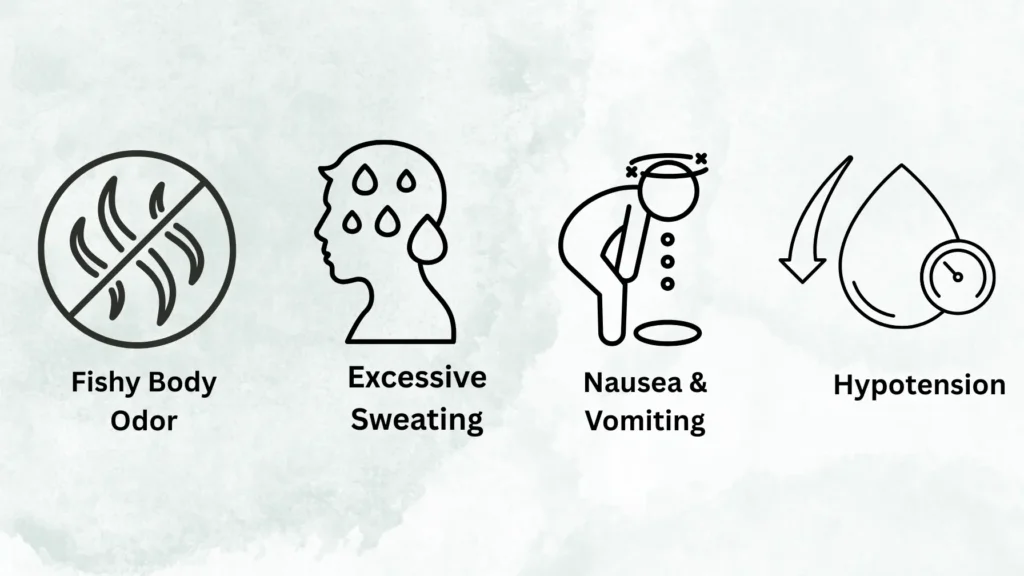
While choline is essential for pregnancy, too much choline can lead to side effects like:
1. Fishy Body Odor
Fishy body odor is one of the most common side effects of excessive choline intake, and it’s primarily due to the body’s inability to metabolize choline properly when taken in very high amounts. This condition is medically referred to as trimethylaminuria or “fish odor syndrome.”
Why It Happens:
- Choline Breakdown: Trimethylamine (TMA) is a strong, fishy-smelling compound that is one of the byproducts of the body’s processing of choline. TMA is normally broken down by the liver into a less pungent substance, but when too much choline is consumed, the liver is overworked and TMA accumulates in the blood.
- Impaired Metabolism: Some people may have a genetic variation that impairs the liver’s ability to process TMA, causing it to accumulate in the body and be released through the skin, breath, and urine, giving off the characteristic fishy smell.
Impact During Pregnancy:
- A fishy body odor can be embarrassing and socially awkward, but it is not dangerous in and of itself. It is crucial to remember that this indicates an excessive intake of choline, which may be dangerous if left unchecked.
- Prevention: It’s crucial to follow the daily choline intake guidelines and refrain from taking supplements without first talking to a healthcare professional in order to prevent this.
2. Excessive Sweating

Excessive sweating, or hyperhidrosis, can also occur with too much choline in the body. This is another side effect that results from the body attempting to excrete excess choline through various pathways, including perspiration.
Why It Happens:
- Choline’s Effect on the Sweat Glands: Choline is involved in the body’s nervous system function, and excessive choline can overstimulate the sweat glands. As the body works to eliminate excess choline, it can trigger an overactive response from the sympathetic nervous system, which controls sweating.
- Regulation of Temperature: The body’s ability to regulate temperature may be altered due to high choline levels, causing increased sweat production to try and cool the body down.
Impact During Pregnancy:
- Increased Discomfort: Pregnancy already leads to hormonal changes that may result in sweating, so excessive sweating from choline intake can make the discomfort worse, especially during warm weather or physical activity.
- Management: If sweating becomes excessive, reducing choline intake and consulting with a healthcare provider can help manage this symptom.
3. Nausea and Vomiting
Nausea and vomiting are common pregnancy symptoms, but they can also occur as a result of excessive choline intake. When too much choline is consumed, the body can experience gastrointestinal distress, which can lead to feelings of nausea and even vomiting.
Why It Happens:
- Choline’s Effect on the Digestive System: Choline, when consumed in high amounts, can irritate the stomach and the intestines, causing digestive issues such as nausea, vomiting, and sometimes diarrhea. The body may respond to this overload of nutrients by attempting to expel them through vomiting.
- Cholinergic Overload: Choline is involved in the production of acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter that controls muscle contractions in the digestive tract. An excess of choline can overstimulate the digestive muscles, leading to nausea and vomiting.
Impact During Pregnancy:
- Pregnant women are already susceptible to nausea due to morning sickness (especially in the first trimester), so excessive choline can exacerbate these symptoms.
- Management: If nausea and vomiting persist, it’s crucial to adjust choline intake and consult a healthcare provider. Reducing the use of choline supplements or adjusting dietary intake can help alleviate the discomfort.
4. Low Blood Pressure (Hypotension)

Dizziness, fainting, and exhaustion are symptoms of low blood pressure, also known as hypotension, a condition in which the blood pressure falls below the normal range. Particularly in the later stages of pregnancy, when the circulatory system experiences significant changes, an excessive choline intake can result in an excessive drop in blood pressure.
Why It Happens:
- Choline and Blood Vessel Dilation: Choline plays a role in acetylcholine production, which is responsible for the communication between nerves and muscles. An excess of acetylcholine can lead to the relaxation and dilation of blood vessels, causing a drop in blood pressure.
- Increased Blood Flow to Tissues: Although this is advantageous in certain situations, excessive vasodilation can result in a decrease in systemic vascular resistance, which can cause hypotension and impact the baby’s ability to receive oxygen and nutrients.
Impact During Pregnancy:
- Pregnant women experience lower blood pressure naturally, especially in the first and second trimesters. Adding excessive choline into the mix may exacerbate hypotension, making a woman feel lightheaded, dizzy, or faint. This is particularly concerning as it can affect a woman’s ability to function properly and may lead to fainting or falls.
- Management: Monitoring and controlling choline intake is crucial, especially if you already experience low blood pressure. Drinking plenty of water and maintaining a balanced, moderate diet can help prevent excessive drops in blood pressure.
The upper tolerable intake level for choline is set at 3,500 mg per day, which is significantly higher than the recommended intake. Always ensure that you stay within the advised limits, especially when using supplements.
Conclusion: How Much Choline for Pregnancy
How much choline for pregnancy is a vital question, as this nutrient plays an integral role in the health of both mother and baby. It promotes the growth of the brain, lessens the chances of birth defects and improves the health of the placenta. This is because whether you attain your required amount of choline by diet, supplementation or both, it is important to make sure you attain the required amount. A healthy pregnancy should always be accompanied by checking with your healthcare provider to see how your unique needs are being met.
Explore more on Pregnancy Must –









